Brain tumour diagnosis
There are several ways that a brain tumour diagnosis can be made. If your doctor (GP or A&E doctor) suspects you have a brain tumour, they will refer you to a specialist, such as a neurologist. These are specialists in brain and nerve disorders. If they suspect a child has a brain tumour, they will refer them to a paediatrician.
Click on the links below to find out more about brain tumour diagnosis by these and other medical professionals.

Neurological examination
What to expect when referred to a specialist for a neurological examination.

Eye tests
Learn what optometrists look for and how to prepare for your eye test.
Diagnostic Scans
Get details about MRI and CT scans, which can provide a detailed 3-D image of the brain.
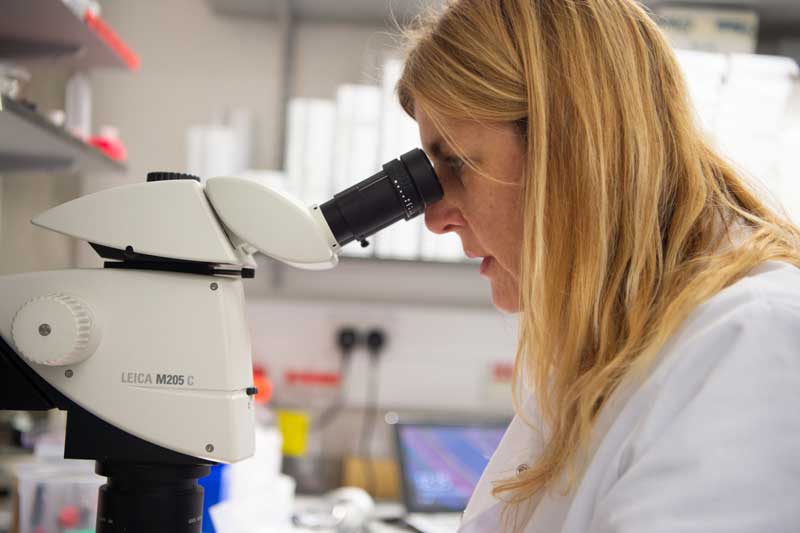

What is a biopsy?
Learn how taking a small sample of the tumour can aid diagnosis of tumour type.

Biomarkers
Biomarkers may help predict tumour growth or how well you may respond to some treatments.
Grading
Brain tumours are graded from 1 to 4 depending on how they are likely to behave. Find out more.

Get your free Information Pack today
If you or someone you love has been diagnosed with a brain tumour and you don’t know which way to turn, start with our Information Pack.
Brain tumour diagnosis
Sometimes brain tumours are discovered during tests for other symptoms. For example, they can sometimes be discovered during eye tests for glasses.
But, if you are experiencing signs and symptoms and you are referred to a specialist, one or more of the various tests might be used in your brain tumour diagnosis.
You can click on the links above to find out more about each test. But, for a general overview, we’ll briefly discuss these brain tumour diagnosis methods here.
Neurological examination
While this might sound like a scan, it is more of a physical exam. Your doctor will ask you about your health and your symptoms as well as check your nervous system. This will involve checking things like your vision, hearing, and reflexes.
Eye test
Eye tests usually diagnose a brain tumour by either identifying swelling of the optic disc or pressure on the optic nerve. The optician will usually check your vision, look at your eye muscles, and look at the inner and outer parts of your eyes.
Diagnostic scan
These are scans that can create an image of the inside of your head. There are two main types of scan that can do this. Usually you’ll have a CT scan, which is a Computerised Tomography scan, or you’ll have an MRI scan, which is a Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan.
Biopsy
A biopsy is where a small sample or the tumour is taken for study in a lab. There are several ways that this can be done, and it will depend on your particular case. A biopsy sample could help to understand the type of tumour as well as its grade, which can help to decide which treatment is best for you. A biopsy is also good for running biomarker tests.
Biomarker
This term is actually a shortening of the phrase, ‘biological marker.’ This type of test indicates a certain process happening in the body. It can be used in brain tumour diagnosis to detect the type of tumour, predict how quickly it might grow, and estimate how you might respond to treatment.