Brain cells
The human body is composed of trillions of cells. Every organ in our body is made up of particular types of cells which carry out specific functions. The two main types of cells found in the human brain are neurons and glial cells.
On this page, we’ll take a closer look at brain cells, covering:
Neurons and glial cells
Throughout the brain and spinal cord we all have nerve cells called ‘neurons’, which transmit ‘messages’ (electrical and chemical signals). Glial cells are cells that surround our neurons. They support and protect the neurons, provide the neurons with oxygen and nutrients, and remove dead cells. Glial cells are much smaller than neurons and we have many more glial cells than neurons.
There are different types of glial cells, each of which plays a different role in supporting the neurons. The main types are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells.
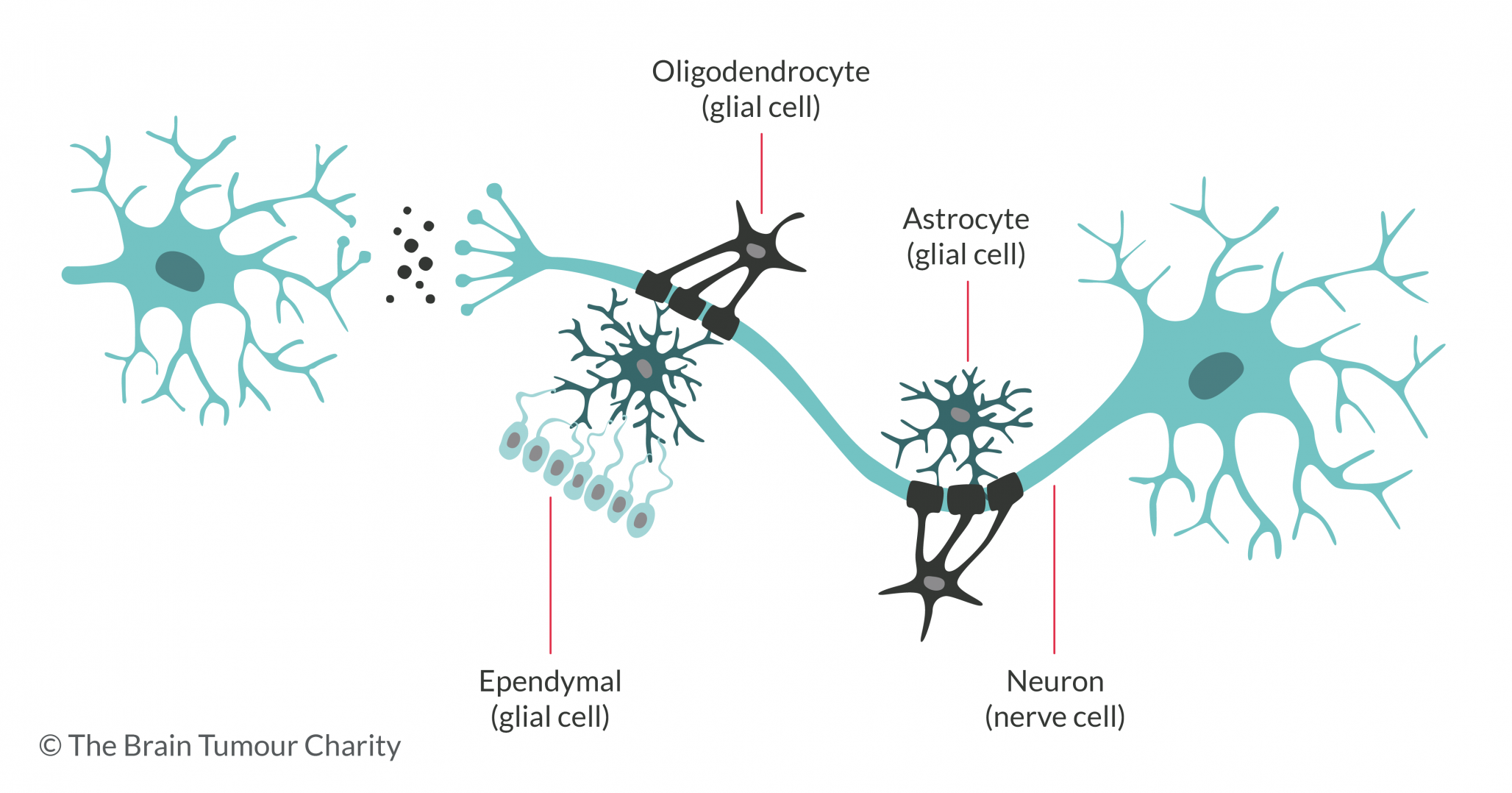
Brain cells and brain tumours
Brain tumours can develop from any of these types of glial cells. Glioma is the collective name for this group of tumours.
However, gliomas will also have a more specific name depending on which type of glial cell the tumour grows from:
- Astrocytomas are brain tumours that grow from astrocytes
- Oligodendrogliomas are brain tumours that grow from oligodendrocytes
- Ependymomas are brain tumours that grow from ependymal cells.
Some other types of brain tumour
- Vestibular shwannomas or acoustic neuromas are brain tumours that grow from schwann cells
- Meningiomas are tumours that grow from arachnoid cap cells, which are within the membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord, known as the meninges
- Haemangioblastomas are tumours that grow from blood vessel cells
- CNS lymphomas grow from a type of white blood cell known as a lymph cell
- Embryonal tumours and germ cell tumours develop from left over cells from the early stages of development.
To learn more about how tumours are diagnosed and what differentiates them, see here: https://www.thebraintumourcharity.org/brain-tumour-diagnosis-treatment/how-brain-tumours-are-diagnosed
How brain tumours form
Normal brain cell division and growth
The images below show normal cell division and growth and what happens when there is abnormal cell division and growth, which can lead to the development of a brain tumour.
Signals from your genes tell your cells when to grow and when to stop growing, when to divide and when to die (a process know as apoptosis).. Therefore your cells normally grow in a controlled way.
If these signals are not there, our bodies have further checkpoints to stop cells dividing in an uncontrolled way.
When a cell divides, it has to copy its genes to put into the new cell. Mutations are mistakes that are sometimes made when copying the genes.
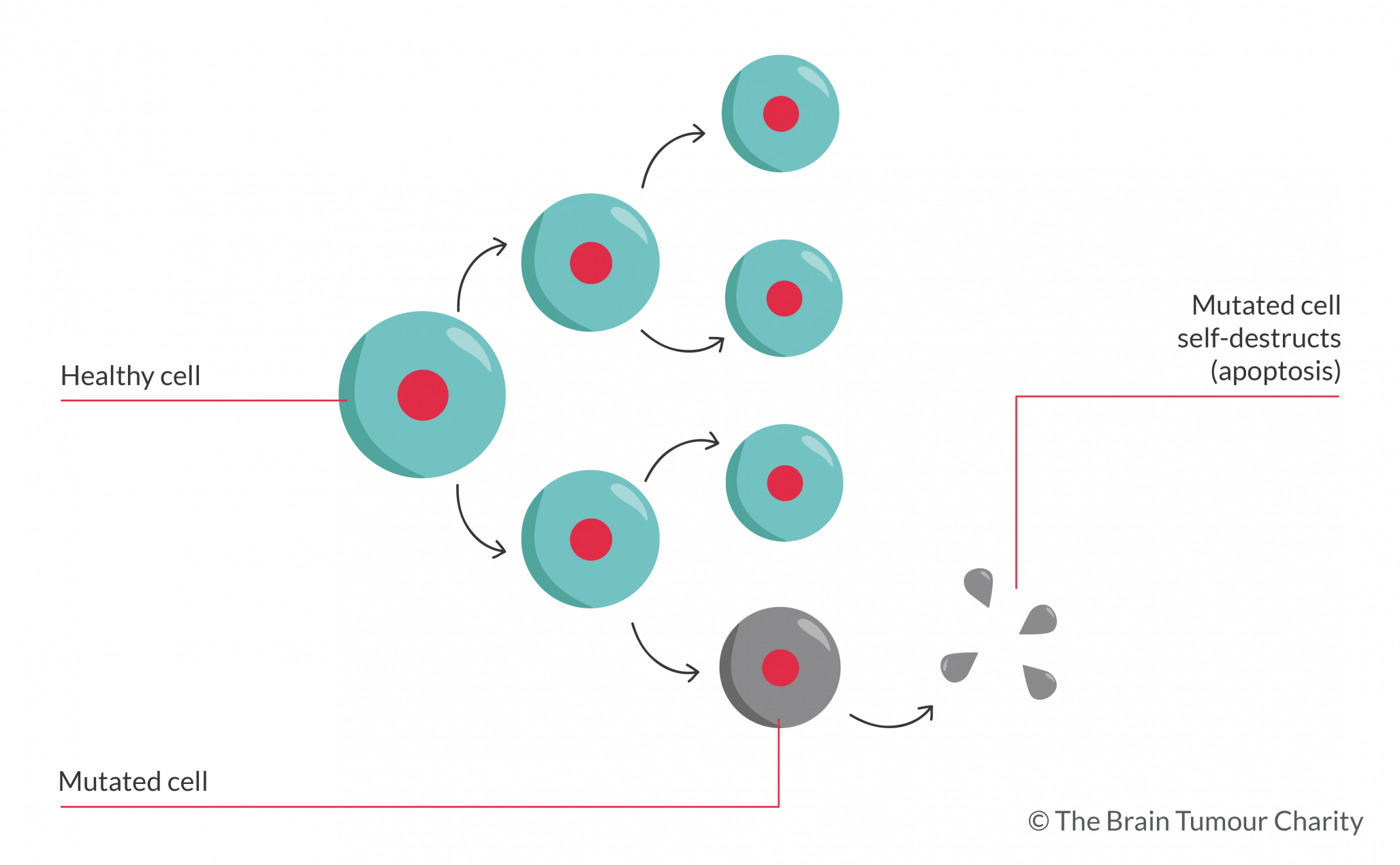
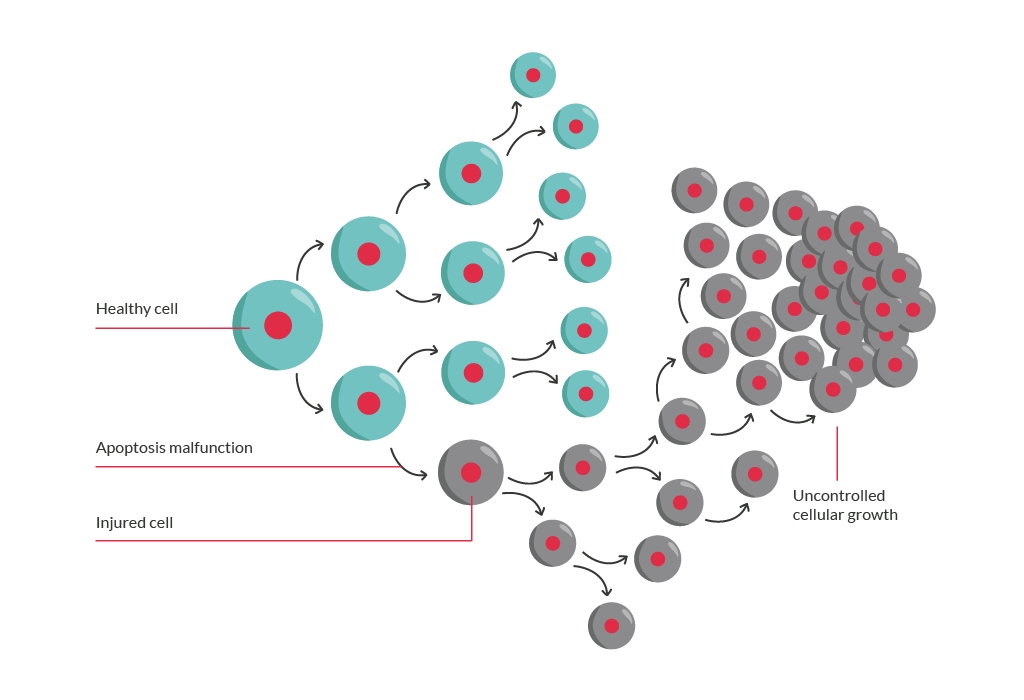
Abnormal brain cell division and growth, leading to the development of a brain tumour
Many mutations don’t have any obvious effects, but if a mistake happens in a gene that helps to control how a cell grows and divides, it can cause the cell to grow uncontrollably and a tumour to grow.
This could be by either making the cell think it is receiving a growth signal even when it’s not, or by shutting down the checkpoints that would normally stop the cell from dividing. As a result, the cell continues to divide.
Each of the new cells formed will also have this change (mistake) in the gene and so will also keep dividing when it shouldn’t. As a result, more and more cells keep dividing and develop into a brain tumour.
Support and Information Services
Research & Clinical Trials Information
You can also join our active online community.
In this section

Get support
If you need someone to talk to or advice on where to get help, our Support and Information team is available by phone, email or live-chat.
Recommended reading
Share your experiences and help create change
By taking part in our Improving Brain Tumour Care surveys and sharing your experiences, you can help us improve treatment and care for everyone affected by a brain tumour.
